Sound Insulation For Sulfur-Recovery Units
This article was written by Mike Bannon & Frank Kaputa

In 2014 Thermaxx was hired to manufacture sound attenuation jackets for sulfur-recovery compressors located at an oil refinery in South America. Thermaxx tested and ultimately specified a certain combination of materials in order to reduce the compressor noise levels down to the customer’s desired decibel level.
Thermaxx engineers conducted the study in a highly sophisticated sound studio utilizing high-tech sound-analyzing equipment and software. The data listed below represents our Engineer’s findings.
Sulfur Recovery Compressor Insulation Jackets
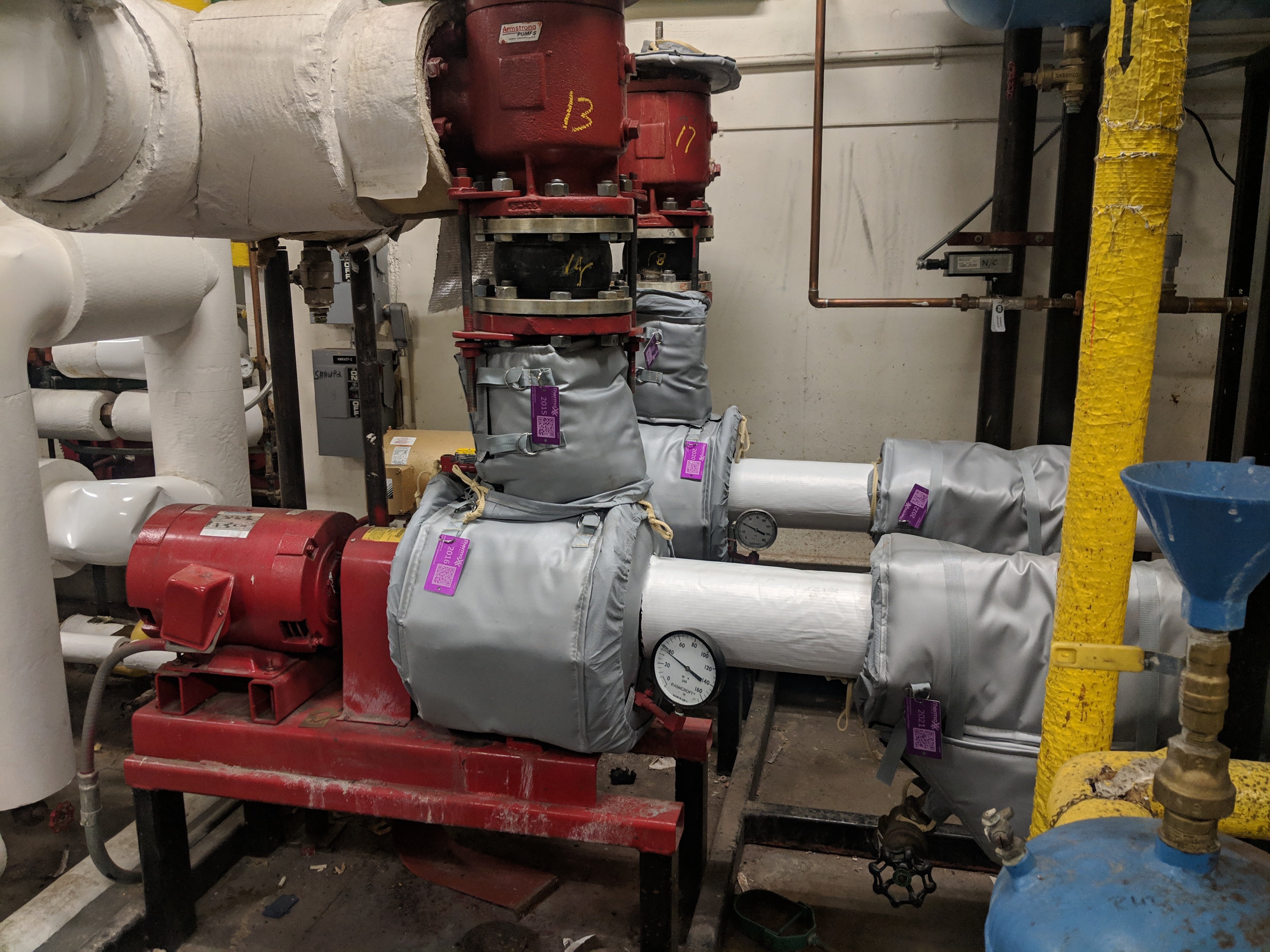
The sulfur-recovery compressor jacket system consists of two jackets – an inner jacket and an outer jacket. The inner jacket is fashioned directly to the compressor box and outer jacket is laid on top of the inner jacket and fashioned to the inner jacket and the compressor box. Each jacket consists of a layer of one-inch needled fiberglass, two layers of ⅛-inch silent tread (recycled tires) and two layers of ⅛-inch mass loaded vinyl. These materials are covered with an acid resistant cover. The jackets just specified were tested in our Thermaxx sound studio. The following chart lists the decibel drops per jacket at different frequencies. With a two-jacket system, as the one manufactured for South America Oil Refinery sulfur-recovery compressors, the decibel drops will be doubled.
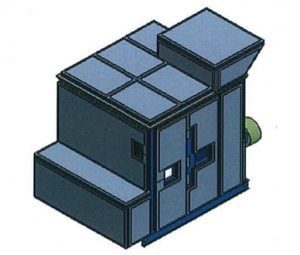

CAD Drawings of Sulfur-Recovery Compressors with Jackets
The relationship between coefficient C and decibel drop d is:
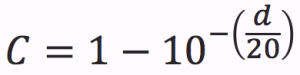
Example: for a 23.1 dB drop, the coefficient is 0.93:
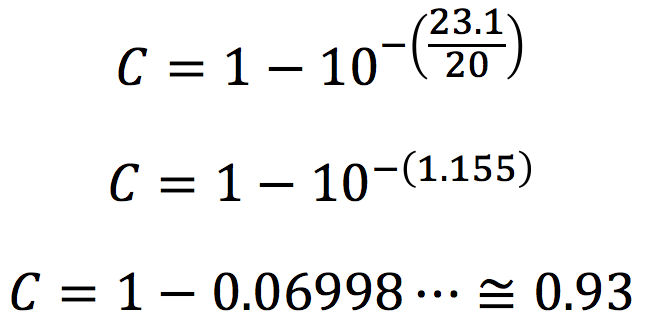
Therefore, the coefficient for this material combination at 1 kHz is 0.93. This test is repeated for the frequencies 125 Hz, 250 Hz, 500 Hz, 1 kHz, 2 kHz, and 4 kHz.
| Frequency | 125 Hz | 250 Hz | 500 Hz | 1 kHz | 2 kHz | 4 kHz |
| dB drop | 19.4 | 21.6 | 22.0 | 23.1 | 22.9 | 22.1 |
| coefficient | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
Using the coefficient to Calculate Decibel Drop
To determine the decibel drop (d) with the material at the given frequency, we can use the coefficient (C) in this formula:
![]()
Example: for a coefficient 0.78, the decibel drop is 13:

If the material is doubled-up, the decibel drop is doubled. We can determine the new coefficient (C2) from the single-layer coefficient (C) with the formula:
![]()
The chart below represents the decibel drops for a two-jacket system.
| Frequency | 125 Hz | 250 Hz | 500 Hz | 1 kHz | 2 kHz | 4 kHz |
| Single-layer coefficient | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
| Double-layer coefficient | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | 0.995 | 0.995 | 0.994 |
| Double-layer dB drop | 38.8 | 43.2 | 44.0 | 46.2 | 45.8 | 44.2 |
Once installed, the two-layer Thermaxx jacket will greatly reduce the noise levels emitted from the sulfur-recovery compressors.
Learn more about Thermaxx Sound Insulation or Contact Us!
Categories
- removable insulation
- thermaxx jackets
- energy savings
- savings
- energy efficiency
- safety
- pipe insulation
- energy
- case study
- insulation materials
- thermal insulation
- heat loss survey
- heat loss
- energy loss
- hot insulation
- fiberglass
- installation
- steam
- New York
- custom insulation
- NYC Case Study
- boiler
- university
- Connecticut
- reusable insulation






